Tag: Featured
-

From Pachyderm: Kansas Senate Candidates
From the Wichita Pachyderm Club this week: Republican primary candidates for Kansas Senate were invited to participate in a forum.
-

WichitaLiberty.TV: News media, hollow Kansas government, ideology vs. pragmatism
In this episode of WichitaLiberty.TV: New outlets for news, and criticism of the existing. Is Kansas government “hollowed out?” Ideology and pragmatism.
-

Candidate forum: Kansas Senate and Sedgwick County Commission
The Sedgwick County Republican Party held a candidate forum. Invited were candidates for Kansas Senate, district 27, and Sedgwick County Commission, district 3.
-

David Dennis, gleeful regulatory revisionist
David Dennis, candidate for Sedgwick County Commission, rewrites his history of service on the Kansas State Board of Education.
-

In Wichita, Meitzner, Clendenin sow seeds of distrust
Comments by two Wichita city council members give citizens more reasons to be cynical and distrusting of politicians.
-

Kansas government ‘hollowed-out’
Is Kansas government “hollowed-out” even though spending is rising?
-
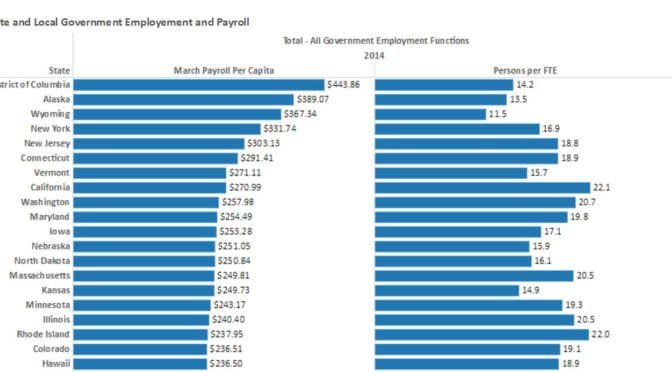
State and local government employee and payroll
Considering all state and local government employees in proportion to population, Kansas has many, compared to other states, and especially so in education.
-

Kansas City Star as critic, or apologist
An editorial in the Kansas City Star criticizes a Kansas free-market think tank.
-

Wichita water statistics update
With adequate river flow every day, the Wichita ASR water project produced water equivalent to six days design capacity during May 2016.
-

Wichita teachers union president on video
The president of United Teachers of Wichita has been caught on video expressing thoughts that can’t be comforting to Wichita parents with children in the state’s largest school district.
-

Kansas Supreme Court: Making law, part 3
Do the justices on the Kansas Supreme Court make new law? Yes, and here is another example.
-

From Pachyderm: Judicial candidates
From the Wichita Pachyderm Club this week: Republican primary candidates participated in an 18th Judicial District Candidates’ Forum. This is an audio presentation recorded on June 24, 2016.