Tag: Pete Meitzner
-
Wichita in ‘Best Cities for Jobs 2018’
Wichita continues to decline in economic vitality, compared to other areas.
-

Wichita metropolitan area population in context
The growth of population in Wichita compared to other areas.
-

WichitaLiberty.TV: John Todd and the fight against blight
John Todd explains how cities in Kansas are seeking additional power to seize property, and tells us why we should oppose this legislation.
-

Property under attack in Kansas
Local governments in Kansas are again seeking expanded power to seize property.
-

Growing the Wichita economy
Wichita leaders are proud of our region’s economic growth. Here are the numbers.
-

CID and other incentives approved in downtown Wichita
The Wichita City Council approves economic development incentives, but citizens should not be proud of the discussion and deliberation.
-

WichitaLiberty.TV: News media, hollow Kansas government, ideology vs. pragmatism
In this episode of WichitaLiberty.TV: New outlets for news, and criticism of the existing. Is Kansas government “hollowed out?” Ideology and pragmatism.
-

In Wichita, Meitzner, Clendenin sow seeds of distrust
Comments by two Wichita city council members give citizens more reasons to be cynical and distrusting of politicians.
-

In Wichita, revealing discussion of property rights
Reaction to the veto of a bill in Kansas reveals the instincts of many government officials, which is to grab more power whenever possible.
-

In Wichita, open records relief may be on the way
A new law in Kansas may provide opportunities for better enforcement of the Kansas Open Records Act.
-

WichitaLiberty.TV: Kansas revenue and spending, initiative and referendum, and rebuliding liberty
The Kansas Legislature appears ready to raise taxes instead of reforming spending. Wichita voters have used initiative and referendum, but voters can’t use it at the state level. A look at a new book “By the People: Rebuilding Liberty Without Permission.”
-
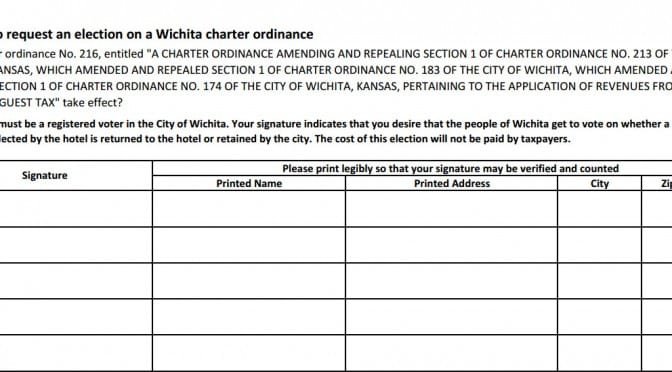
Wichita has examples of initiative and referendum
Citizens in Wichita have been busy exercising their rights of initiative and referendum at the municipal level. The Kansas Legislature should grant the same rights to citizens at the state level.