Tag: Wichita city government
-

Wichita to grant property and sales tax relief
Several large employers in Wichita ask to avoid paying millions in taxes, which increases the cost of government for everyone else, including young companies struggling to break through.
-

Wichita bridges, well memorialized
Drivers — like me — on East Twenty-First Street in Wichita are happy that the work on a small bridge is complete, but may not be pleased with one aspect of the project.
-

Beware of government arts spending
Art is too important to be dependent on politicians and injecting politics into anything inevitably tarnishes it, writes Lawrence W. Reed of Foundation for Economic Education.
-

WichitaLiberty.TV: Wichita and Kansas economics, and government investment
Wichita sells a hotel, more subsidy for downtown, Kansas newspaper editorialists fall for a lobbyist’s tale, how Kansas can learn from Arizona schools, and government investment.
-
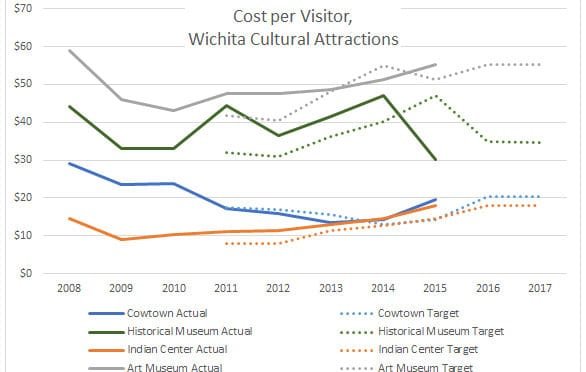
Cost per visitor to Wichita cultural attractions
Wichitans might be surprised to learn the cost of cultural attractions.
-

CID and other incentives approved in downtown Wichita
The Wichita City Council approves economic development incentives, but citizens should not be proud of the discussion and deliberation.
-

Wichita has no city sales tax, except for these
There is no Wichita city retail sales tax, but the city collects tax revenue from citizens when they buy utilities, just like a sales tax.
-

CID and other incentives proposed in downtown Wichita
A proposal for a community improvement district in downtown Wichita includes a public hearing, but much information the public needs is missing.
-

Wichita water statistics update
With adequate river flow every day, the Wichita ASR water project produced water equivalent to six days design capacity during July 2016.
-

In Wichita, your house numbers may become illegal
Thousands of Wichita homeowners may soon be lawbreakers if the city council follows its staff’s recommendation.
-

Wichita water statistics update
With adequate river flow every day, the Wichita ASR water project produced water equivalent to seven days design capacity during June 2016.
-

WichitaLiberty.TV: News media, hollow Kansas government, ideology vs. pragmatism
In this episode of WichitaLiberty.TV: New outlets for news, and criticism of the existing. Is Kansas government “hollowed out?” Ideology and pragmatism.