Tag: Downtown Wichita revitalization
-

Living in downtown Wichita
Wichita economic development officials use a circuitous method of estimating the population of downtown Wichita, producing a number much higher than Census Bureau estimates.
-

Downtown Wichita report omits formerly prominent data
The new State of Downtown Wichita report for 2017 is missing something. What is it, and why is it missing?
-

WichitaLiberty:TV: Wichita economy, Kansas schools
Karl Peterjohn and Bob Weeks discuss some statistics regarding downtown Wichita and then the Kansas school finance court decision.
-

Wichita, youthful and growing from the core
A letter writer tells Wichitans that “We have an opportunity to show the country the future of Wichita is youthful and bright, and its growing from the core out.”
-
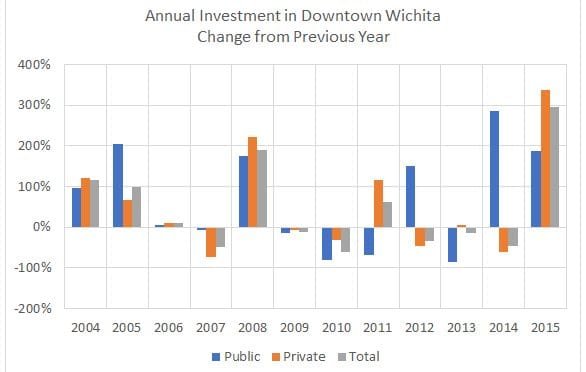
Investment in Downtown Wichita
Charts and tables of investment in Downtown Wichita.
-
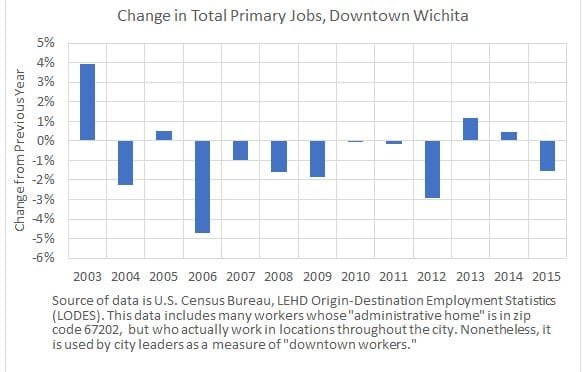
Downtown Wichita jobs decline
By the measure of jobs used by the City of Wichita, downtown jobs declined in 2015.
-

WichitaLiberty.TV: Century II, Again
Karl Peterjohn and Bob Weeks continue discussing Century II, Wichita’s convention and performing arts center. But first, some unfortunate economic news for Wichita. Episode 166, broadcast September 24, 2017.
-

Century II: The consultant’s disclaimer
The report produced for the City of Wichita on Century II has a disclaimer that absolves pretty much everyone from any accountability.
-

Century II resource center
A resource of information about the Century II Performing Arts and Convention Center in Wichita.
-

WichitaLiberty.TV: Century II, Its Future
Community influencer John Todd joins Karl Peterjohn and Bob Weeks to discuss Century II, Wichita’s convention and performing arts center.
-

WichitaLiberty.TV: Wichita and Kansas economies
In this episode of WichitaLiberty.TV: Bob Weeks and Karl Peterjohn discuss issues regarding the Wichita and Kansas economies.
-

In Wichita, not your tax dollars
At a Wichita City Council meeting, citizens are told, “These tax dollars are not your tax dollars.”